Introduction
In a world where our diets are as varied as the apps on our smartphones, understanding blood sugar levels can feel like trying to decode a secret language. For those managing diabetes, pre-diabetes, or just curious about their health, knowing what constitutes a “normal” blood sugar level is crucial. Imagine your blood sugar as a rollercoaster—sometimes thrilling, sometimes a bit too high for comfort. This article will unravel the complexities behind blood sugar levels and provide a comprehensive chart that outlines what to aim for across different demographics.
Let’s kick things off with the basics. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary fuel for our bodies. It’s sourced from the carbohydrates we eat, turning our meals into energy. However, just like too much caffeine can make you jittery, too much glucose can lead to health issues. Knowing the ideal range for blood sugar can help you feel your best and avoid potential complications.
So, what are normal blood sugar levels? According to the World Health Organization, a normal fasting blood sugar level sits between 70 mg/dL and 100 mg/dL. If you’ve just polished off a buffet, your levels will naturally rise. It’s normal for glucose levels to fluctuate, but in this article, we’ll provide a handy chart detailing what’s considered “normal” across various age groups and conditions.
The journey to understanding your blood sugar begins here—let’s navigate through this essential health topic! Whether you’re a parent checking your child’s levels or an adult keeping tabs on your own health, this guide is a must-read. Get ready to explore the world of glucose—it’s about to get informative and maybe a bit fun!
Understanding your blood sugar levels is like having the secret recipe to your personal health. The more you know, the more control you have over your body. So, let’s unravel this mystery together and empower you to take charge of your health!

To help you keep track of your blood sugar levels, consider investing in a Glucometer Blood Sugar Testing Kit. It’s a handy tool that can help you monitor your glucose levels easily, ensuring you stay on top of your health game!
Summary
This article explores the intricate world of blood sugar levels, providing a detailed chart that breaks down what constitutes normal blood glucose levels across various age groups and health conditions. From fasting glucose levels to post-prandial measures, understanding these metrics is essential for effective diabetes management and overall health.
The article will cover the significance of monitoring blood sugar levels, the impact of age on glucose targets, and guidelines for individuals with diabetes, pre-diabetes, and even pregnant women. With practical tips for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how to interpret their readings and manage their health proactively.
By the end of this article, you will not only be equipped with knowledge but also empowered to take control of your health journey. After all, knowing your numbers is the first step toward a healthier you! Whether you’re breaking down the barriers of diabetes or simply aiming for better overall wellness, this guide is your go-to resource for blood sugar management. Prepare to demystify those numbers and navigate your health like a pro!

Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels?
Ah, blood sugar levels! Think of them as the Goldilocks zone for your health—not too high, not too low, but just right! So, what do we mean by “normal”? The World Health Organization (WHO) provides a clear guideline: a normal fasting blood sugar level sits between 70 mg/dL and 100 mg/dL. After a meal, your blood sugar level can rise, but ideally, it should not exceed 140 mg/dL two hours post-meal.
But hold your horses! Blood sugar levels can vary significantly depending on whether you’re a non-diabetic or living with diabetes. For individuals without diabetes, the goal is straightforward. However, for those managing diabetes, the target ranges can differ. For example, diabetics often aim for fasting levels between 80 mg/dL and 130 mg/dL, while post-meal levels should ideally be under 180 mg/dL. It’s like trying to hit a moving target, but with the right guidance, you can hit the bullseye!
Now, let’s throw a little WHO wisdom into the mix. According to their guidelines, a two-hour plasma glucose level above 200 mg/dL indicates hyperglycemia, which is a fancy term for high blood sugar. Knowing these numbers can help you stay on track and avoid complications down the line.
Understanding what constitutes normal blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining health.

Importance of Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels isn’t just a suggestion; it’s crucial for effective diabetes management. Think of it as your health’s GPS—guiding you away from potential roadblocks. When your blood sugar levels fluctuate too much, the consequences can be serious. High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, can lead to symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. Over time, it can cause severe complications, including nerve damage, kidney disease, and heart issues. Yikes!
On the other hand, low blood sugar levels, known as hypoglycemia, can be equally alarming. Symptoms like shakiness, dizziness, and confusion can occur, and if left untreated, it could lead to seizures or even loss of consciousness. So, it’s essential to keep an eye on those numbers!
Here’s a startling statistic: according to the CDC, nearly 1 in 10 Americans has diabetes. That’s about 34 million people! This makes understanding and monitoring blood sugar levels not just a personal concern but a public health issue.
By keeping tabs on your blood sugar, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve your quality of life. So, whether you’re using a glucometer or a Continuous Glucose Monitor, make it a habit to check those numbers. After all, knowledge is power, and in this case, it’s also your ticket to a healthier life!
Stay tuned as we continue to unravel the mysteries of blood sugar levels and help you understand what those numbers truly mean for your health!
Normal Blood Sugar Levels for Adults
Understanding normal blood sugar levels is crucial for adults, especially those managing diabetes. Here’s a handy chart to help you know what to aim for:
| Age Group | Fasting Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) | Post-Prandial Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| 18 – 50 years | 70 – 99 | < 140 |
| 51 – 60 years | 70 – 105 | < 150 |
| 61 – 90 years | 70 – 115 | < 160 |
These numbers serve as a guideline for healthy blood glucose management. It’s essential to keep in mind that lifestyle factors can significantly impact these levels.

Diet plays a starring role in blood sugar control. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber and low in refined sugars can help maintain those levels. Regular physical activity is also crucial. It can enhance insulin sensitivity, making it easier for your body to use glucose. Consider checking out some Diabetes Cookbooks for delicious, healthy recipes that will keep your meals both tasty and blood sugar-friendly!
Stress management is another vital factor. Stress hormones can spike blood sugar levels, making it important to find ways to unwind. Whether it’s yoga, meditation, or simply binge-watching your favorite show, take time for yourself!

Normal Blood Sugar Levels for Seniors
As we age, our bodies change, and so do our blood sugar goals. Seniors often require more personalized targets. Here’s a brief overview for older adults:
| Age Group | Fasting Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) | Post-Prandial Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| 65 years and older | 80 – 180 | < 180 |
Older adults may be more susceptible to fluctuations in blood sugar levels due to factors like medications, reduced physical activity, or changes in eating habits. Therefore, monitoring becomes increasingly important.
Additionally, seniors often experience a decline in their ability to recognize symptoms of low blood sugar, making regular checks even more critical. Managing these levels can help prevent complications like cognitive decline and cardiovascular issues.

Blood Sugar Levels During Pregnancy
Pregnancy brings a unique set of challenges, especially regarding blood sugar levels. Monitoring glucose is vital for the health of both mother and baby. Here’s what to aim for:
| Condition | Blood Glucose Level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Fasting levels | 70 – 89 |
| Levels before meals | < 90 |
| Levels 1 hour after meals | < 140 |
| Levels 2 hours after meals | < 120 |
Keeping blood sugar levels in check during pregnancy can prevent gestational diabetes, which can pose risks to both mother and child. It’s essential for expectant mothers to work closely with healthcare providers to track their levels and adjust their diet and activity as needed.

Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Diet and Nutrition
Let’s talk carbs—those delicious little energy boosters! But, beware! Not all carbs are created equal. Simple carbs, like sugary treats, can send your blood sugar levels soaring faster than a roller coaster. On the flip side, complex carbs, found in whole grains and legumes, release glucose more slowly, keeping your levels stable.
Consider this: when you consume a meal high in refined carbs, your body may struggle to keep up, leading to spikes in blood sugar. Aim for a balanced plate with lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fiber. Think of it as giving your body a team of superheroes to tackle glucose!

Here are some dietary tips to keep your glucose levels in check:
- Portion Control: Keep an eye on serving sizes to avoid overindulgence.
- Eat Regularly: Don’t skip meals! Regular eating helps maintain stable levels.
- Choose Fiber-rich Foods: They help slow down glucose absorption. You might want to try Whole Grain Pasta for a tasty, fiber-rich option!
- Stay Hydrated: Water aids in digestion and can help regulate glucose levels.
Managing your diet effectively can be a game-changer for your blood sugar levels. Making informed choices can keep you feeling energetic and happy—even if you have to pass on that extra slice of cake!

Physical Activity
Exercise is a fantastic way to keep blood sugar levels in check. Think of it as a glucose vacuum cleaner, sucking up excess sugar from your bloodstream. When you exercise, your muscles use glucose for energy. This helps lower blood sugar levels, especially after meals.
How much should you move? Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. This could be brisk walking, cycling, or even dancing like no one’s watching!
To make it easier to incorporate physical activity into your daily routine, consider these tips:
- Set a Schedule: Block out time in your calendar for exercise. Treat it like an important meeting.
- Find Activities You Enjoy: Whether it’s swimming, hiking, or yoga, pick something fun! You’re more likely to stick with it.
- Buddy Up: Exercise with a friend. Not only is it more fun, but it keeps you accountable.
- Break It Down: If 30 minutes feels daunting, break it into shorter sessions. Three 10-minute walks work just as well!
- Use Your Commute: Walk or bike to work if possible. It’s a great way to sneak in some exercise without it feeling like a chore.
Stress and Sleep
Stress can be a sneaky little culprit when it comes to blood sugar levels. Stress hormones like cortisol can lead to increased blood sugar. So, if you’re feeling overwhelmed, take a breather!
Sleep deprivation also plays a role. Lack of sleep can impair insulin sensitivity, making it harder for your body to manage glucose levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night for optimal health. Consider using a Sleep Mask to block out distractions and help you get those Z’s!
Here are some tips for managing stress and improving sleep quality:
- Practice Mindfulness: Techniques like meditation or deep breathing can help reduce stress levels. Even a few minutes can make a difference.
- Establish a Sleep Routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day. Your body loves consistency!
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: The blue light from screens can mess with your sleep. Consider reading a book instead.
- Regular Exercise: It’s a two-for-one deal! Exercise helps reduce stress and improves sleep quality.
- Create a Sleep-friendly Environment: Keep your bedroom dark, cool, and quiet. A comfy mattress doesn’t hurt either!

By managing stress and ensuring quality sleep, you can help maintain those blood sugar levels in check. After all, who doesn’t want to wake up feeling refreshed and ready to tackle the day?
Monitoring and Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Tools and Techniques for Monitoring
Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for effective diabetes management. There are several methods available to keep those numbers in check. The most common tools include glucometers and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs).
A glucometer is a small device that measures blood glucose levels through a finger prick. Simply place a test strip in the meter, prick your finger, apply a drop of blood, and voilà! You’ll have your reading within seconds.
On the other hand, continuous glucose monitors provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day. They use a tiny sensor inserted under the skin. This method is particularly helpful for tracking trends and understanding how certain foods or activities affect your levels.
Interpreting the results is crucial. Blood sugar levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Here’s a quick reference:
- Normal fasting blood sugar: 70-99 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100-125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher
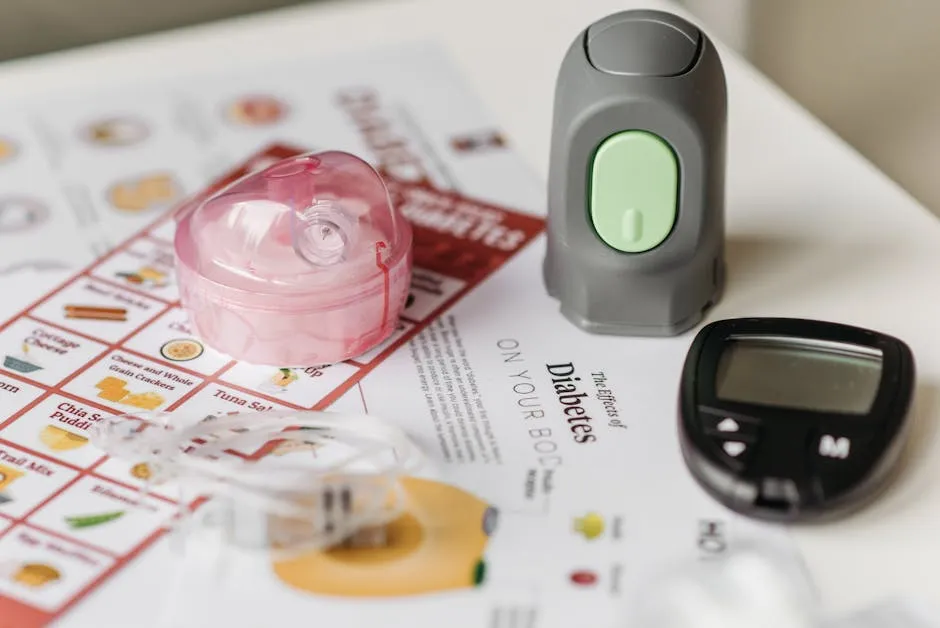

If your levels are consistently outside the normal range, consult a healthcare professional. They can help create a tailored plan that suits your needs.
Strategies for Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Managing blood sugar levels involves a mix of medication and lifestyle modifications. For many, medication is necessary. This may include insulin for type 1 diabetes or oral medications for type 2 diabetes. Always follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding medication and dosages.
Lifestyle modifications can also have a profound impact. Here are some effective strategies:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit processed foods and sugary snacks. For some great ideas, check out the Low Glycemic Index Cookbook!
- Regular Exercise: As mentioned earlier, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity each week. It’s not just good for your body; it’s great for your mind too.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain proper hydration and can assist in regulating blood sugar levels. A Water Bottle with Time Marker can help you stay on track!
- Monitor Portion Sizes: Be mindful of serving sizes to avoid overeating, even with healthy foods.
- Keep a Food Diary: Tracking what you eat can help identify patterns and make it easier to manage your blood sugar.

Incorporating these strategies into your daily life can make a significant difference in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Remember, it’s all about finding a balance that works for you!
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Recognizing when to seek medical advice is crucial. If you experience symptoms of high or low blood sugar, such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, extreme fatigue, or shakiness, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
They can provide guidance on how to manage these episodes effectively. Keeping your healthcare team in the loop will help you stay on track and adjust your management plan as necessary.
In summary, monitoring and managing blood sugar levels involves a mix of tools, techniques, lifestyle changes, and medication. By taking proactive steps, you can maintain your health and enjoy life to the fullest!
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Blood sugar levels can be a bit like a dramatic soap opera—full of unexpected twists and turns! Recognizing the symptoms of high and low blood sugar is essential for managing your health effectively.
Let’s start with high blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia. When your blood sugar levels soar above the norm, you might experience symptoms like increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. If you find yourself guzzling water like a thirsty camel and running to the restroom every few minutes, it’s a sign to check those levels. Prolonged hyperglycemia can lead to serious complications, so don’t ignore the warning signs!
On the flip side, low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can be equally alarming. Symptoms include shakiness, sweating, confusion, and irritability. If you feel dizzy or lightheaded, it’s time to take action. Eating a quick snack with sugar can help stabilize your levels. If left untreated, hypoglycemia can cause fainting or seizures. So be vigilant!
Now, when should you seek medical advice? If you regularly experience symptoms of high or low blood sugar, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional. They can help you develop a personalized plan to manage your blood sugar effectively. Additionally, if you notice sudden changes in your symptoms or blood sugar levels, don’t hesitate to reach out. Remember, better safe than sorry!

Conclusion
In summary, maintaining normal blood sugar levels is vital for overall health, particularly for those living with diabetes or pre-diabetes. Understanding what constitutes a normal range can empower individuals to take charge of their health and make informed decisions. By monitoring blood sugar levels, making dietary and lifestyle changes, and seeking professional guidance when necessary, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications and enjoy a healthier life.
Blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day, influenced by various factors including diet, physical activity, and stress. A consistent monitoring routine is key. Aim for a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables while limiting refined sugars. Regular exercise is also essential; it not only helps manage blood sugar levels but also boosts overall well-being. Remember, you are the captain of your health ship!
If you’re living with diabetes, consider working closely with a healthcare provider. They can help tailor a plan suited to your individual needs. Education is your best ally; understanding how different foods and activities affect your blood sugar can lead to better management and improved health outcomes.
Lastly, don’t forget that mental health plays a role too! Managing your blood sugar can sometimes feel overwhelming, but take it one step at a time. Celebrate small victories, and don’t hesitate to reach out to support groups or professionals when you need assistance. You’ve got this!
FAQs
What is considered a normal blood sugar level?
Normal fasting blood sugar levels generally range from 70 to 100 mg/dL. Post-meal levels should ideally be under 140 mg/dL two hours after eating.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
The frequency of checks varies. For those with diabetes, it’s often recommended to check before meals and at bedtime. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
Common symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. If you experience these, it’s time to check your levels.
Can I manage my blood sugar levels without medication?
Yes, many individuals can manage their blood sugar through dietary changes, regular exercise, and weight management. Always consult a healthcare professional before making changes.
What should I do if my blood sugar levels are too high or too low?
For high levels, drink water and monitor closely. For low levels, consume fast-acting carbohydrates like glucose tablets or juice. If symptoms persist, seek medical advice.
Please let us know what you think about our content by leaving a comment down below!
Thank you for reading till here 🙂
All images from Pexels




